Rhythm guitar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
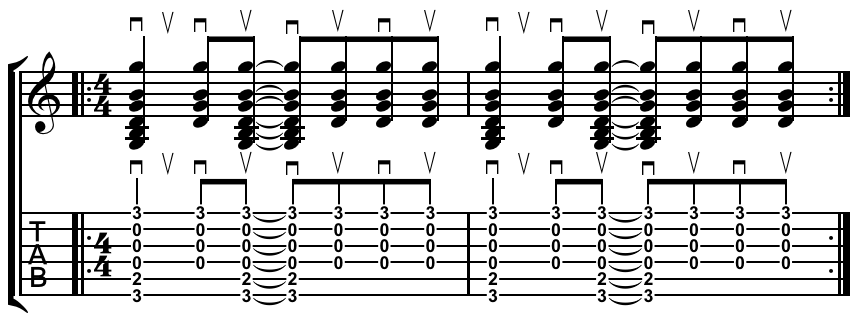

 In music performances, rhythm guitar is a
In music performances, rhythm guitar is a
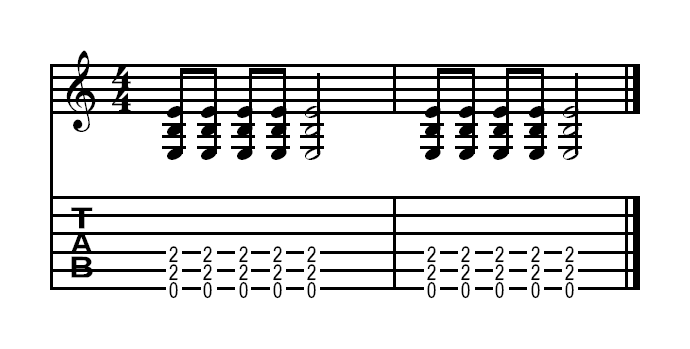 In
In

 Funk utilized the same
Funk utilized the same

technique
Technique or techniques may refer to:
Music
* The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s
*Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s
* ''Technique'' (album), by New Order, 1989
* ''Techniques'' (album), by M ...
and role that performs a combination of two functions: to provide all or part of the rhythmic pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
in conjunction with other instruments from the rhythm section
A rhythm section is a group of musicians within a music ensemble or band that provides the underlying rhythm, harmony and pulse of the accompaniment, providing a rhythmic and harmonic reference and "beat" for the rest of the band.
The rhythm sec ...
(e.g., drum kit
A drum kit (also called a drum set, trap set, or simply drums) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and other auxiliary percussion instruments set up to be played by one person. The player ( drummer) typically holds a pair of matching drumsti ...
, bass guitar
The bass guitar, electric bass or simply bass (), is the lowest-pitched member of the string family. It is a plucked string instrument similar in appearance and construction to an electric or an acoustic guitar, but with a longer neck and ...
); and to provide all or part of the harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However ...
, i.e. the chords
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord (as ...
from a song's chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice ...
, where a chord is a group of notes played together. Therefore, the basic technique of rhythm guitar is to hold down a series of chords with the fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical instrume ...
ting hand while strumming
In music, strumming is a way of playing a stringed instrument such as a guitar, ukulele, or mandolin. A strum or stroke is a sweeping action where a finger or plectrum brushes over several Strings (music), strings to generate sound. On most st ...
or fingerpicking rhythmically with the other hand. More developed rhythm techniques include arpeggios
A broken chord is a chord broken into a sequence of notes. A broken chord may repeat some of the notes from the chord and span one or more octaves.
An arpeggio () is a type of broken chord, in which the notes that compose a chord are played ...
, damping
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples incl ...
, riffs
A riff is a repeated chord progression or refrain in music (also known as an ostinato figure in classical music); it is a pattern, or melody, often played by the rhythm section instruments or solo instrument, that forms the basis or accomp ...
, chord solo
Jazz guitar may refer to either a type of electric guitar or a guitar playing style in jazz, using electric amplification to increase the volume of acoustic guitars.
In the early 1930s, jazz musicians sought to amplify their sound to be hear ...
s, and complex strums.
In ensembles or bands playing within the acoustic, country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
, rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
or metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
genres (among others), a guitarist playing the rhythm part of a composition plays the role of supporting the melodic lines and improvised solos played on the lead instrument or instruments, be they strings, wind, brass, keyboard or even percussion instruments, or simply the human voice, in the sense of playing steadily throughout the piece, whereas lead instruments and singers switch between carrying the main or countermelody and falling silent. In big band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s an ...
music, the guitarist is considered part of the rhythm section, alongside bass and drums
A drum kit (also called a drum set, trap set, or simply drums) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and other Percussion instrument, auxiliary percussion instruments set up to be played by one person. The player (drummer) typically holds a pair o ...
.
In some musical situations, such as a solo singer-guitarist, the guitar accompaniment
Accompaniment is the musical part which provides the rhythmic and/or harmonic support for the melody or main themes of a song or instrumental piece. There are many different styles and types of accompaniment in different genres and styles ...
provides all the rhythmic drive; in large ensembles it may be only a small part (perhaps one element in a polyrhythm
Polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music (cross-rhyth ...
). Likewise, rhythm guitar can supply all of the harmonic input to a singer-guitarist or small band, but in ensembles that have other harmony instruments (such as keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
s) or vocal harmonists, its harmonic input will be less important.
In the most commercially available and consumed genres, electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar (however combinations of the two - a semi-acoustic guitar and an electric acoustic gui ...
s tend to dominate their acoustic cousins in both the recording studio
A recording studio is a specialized facility for sound recording, mixing, and audio production of instrumental or vocal musical performances, spoken words, and other sounds. They range in size from a small in-home project studio large enoug ...
and live venues. However the acoustic guitar remains a popular choice in country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
, western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and especially bluegrass music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music
The term American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as ''traditional music'', ''traditional folk music'', ''contemporary folk music'', ''vernacular music,'' or ...
, and almost exclusively in folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
.
Rock and pop
Rock and pop rhythms
Most rhythms in rock and blues are based on 4/4 time with abackbeat
In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse (regularly repeating event), of the ''mensural level'' (or ''beat level''). The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when listening to a pi ...
; however, many variations are possible. A backbeat is a syncopated
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "place ...
accentuation
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as ...
on the "off" beat. In a simple 4/4 rhythm these are beats 2 and 4. Emphasized back beat, a feature of some African styles, defined rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a genre of popular music that originated in African-American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed predominantly ...
recordings in the late 1940s and so became one of the defining characteristics of rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from Africa ...
and much of contemporary popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
.
Rock and pop harmony
Harmonically, in rock music, the most common way to construct chord progressions is to play major and minor " triads", each comprising a root, third and fifth note of a given scale. An example of a major triad is C major, which contains the notes C, E and G. An example of a minor triad is the A minor chord, which includes the notes A, C and E. Interspersed are some four-note chords, which include the root, third and fifth, as well as a sixth, seventh or ninth note of the scale. The most common chord with four different notes is thedominant seventh
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad tog ...
chord, which include a root, a major third above the root, a perfect fifth above the root and a flattened seventh. In the key of C major, the dominant seventh chord is a G7, which consists of the notes G, B, D and F.
Three-chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice ...
s are common in earlier pop and rock, using various combinations of the I, IV and V chords, with the twelve-bar blues
The 12-bar blues (or blues changes) is one of the most prominent chord progressions in popular music. The blues progression has a distinctive form in lyrics, phrase, chord structure, and duration. In its basic form, it is predominantly based on ...
particularly common. A four chord progression popular in the 1950s is I-vi-ii-V, which in the key of C major is the chords C major, a minor, d minor and G7. Minor
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
*Minor chord
** Barb ...
and modal chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practic ...
s such as I-bVII-bVI (in the key of E, the chords E major, D major, C major) feature in popular music.
 In
In heavy metal music
Heavy metal (or simply metal) is a genre of rock music that developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s, largely in the United Kingdom and United States. With roots in blues rock, psychedelic rock and acid rock, heavy metal bands developed a ...
, rhythm guitarists often play power chord
A power chord (also fifth chord) is a colloquial name for a chord in guitar music, especially electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly played on am ...
s, which feature a root note and a fifth above, or with an octave doubling the root. There actually is no third of the chord. Power chords are usually played with distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
.
Arpeggios
One departure from the basic strummed chord technique is to playarpeggio
A broken chord is a chord broken into a sequence of notes. A broken chord may repeat some of the notes from the chord and span one or more octaves.
An arpeggio () is a type of broken chord, in which the notes that compose a chord are played ...
s, i.e. to play individual notes in a chord separately. If this is done rapidly enough, listeners will tend to hear the sequence as harmony rather than melody. Arpeggiation is often used in folk, country, and heavy metal, sometimes in imitation of older banjo
The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, and usually made of plastic, or occasionally animal skin. Early forms of the instrument were fashi ...
techniques. It is also prominent in 1960s pop, such as The Animals
The Animals (also billed as Eric Burdon and the Animals) are an English rock band, formed in Newcastle upon Tyne in the early 1960s. The band moved to London upon finding fame in 1964. The Animals were known for their gritty, bluesy sound and ...
' "House of the Rising Sun
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
", and jangle pop
Jangle pop is a subgenre of pop rock or college rock that emphasizes jangly guitars and 1960s-style pop melodies. The term originated from Bob Dylan's song " Mr. Tambourine Man", whose 1965 rendition by the Byrds became considered one of the g ...
from the 1980s onwards. Rhythm guitarists who use arpeggios often favor semi-acoustic
A semi-acoustic guitar, hollow-body electric, or thinline is a type of electric guitar that was first created in the 1930s. It has a sound box and at least one electric pickup. The semi-acoustic guitar is different to an acoustic-electric guita ...
guitars and twelve string guitar
A twelve-string guitar (or 12-string guitar) is a steel-string guitar with 12 strings in six courses, which produces a thicker, more ringing tone than a standard six-string guitar. Typically, the strings of the lower four courses are tuned in o ...
s to get a bright, undistorted "jangly" sound.
The Soukous
Soukous (from French '' secousse'', "shock, jolt, jerk") is a genre of dance music from Congo-Kinshasa and Congo-Brazzaville. It derived from Congolese rumba in the 1960s, becoming known for its fast dance rhythms and intricate guitar improv ...
band TPOK Jazz
OK Jazz, later renamed TPOK Jazz (short for ''Tout Puissant Orchestre Kinois de Jazz''), was a Congolese rumba band from the Democratic Republic of the Congo established in 1956 and fronted by Franco. The group disbanded in 1993, but reformed i ...
additionally featured the unique role of ''mi-solo'', (meaning "half solo") guitarist, playing arpeggio
A broken chord is a chord broken into a sequence of notes. A broken chord may repeat some of the notes from the chord and span one or more octaves.
An arpeggio () is a type of broken chord, in which the notes that compose a chord are played ...
patterns and filling a role "between" the lead and rhythm guitars.
Riffs
In some cases, the chord progression is implied with a simplified sequence of two or three notes, sometimes called a "riff
A riff is a repeated chord progression or refrain in music (also known as an ostinato figure in classical music); it is a pattern, or melody, often played by the rhythm section instruments or solo instrument, that forms the basis or accompani ...
". That sequence is repeated throughout the composition. In heavy metal music, this is typically expanded to more complex sequences comprising a combination of chords, single notes and palm muting
The palm mute is a playing technique for guitar and bass guitar, executed by placing the side of the picking hand below the little finger across the strings to be plucked, very close to the bridge, and then plucking the strings while the damp ...
. The rhythm guitar parts in compositions performed by more technically oriented bands often include riffs employing complex lead guitar techniques. In some genres, especially metal, the audio signal from the rhythm guitar's output is often subsequently run through some form of effect pedal or overdriven guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce sound through one or more loudspeakers, which a ...
in order to create a thicker, crunchier sound for the palm-muted rhythms.
Interaction with other guitarists
In bands with two or more guitarists, the guitarists may exchange or even duplicate roles for various songs or severalsections
Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
within a song. In those with a single guitarist, the guitarist may play lead and rhythm at numerous times or simultaneously, by overlaying the rhythm sequence with a lead line.
Crossover with keyboards
Electroniceffects unit
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in el ...
s such as delay pedals and reverb units enable electric guitarists to play arpeggios and take over some of the role of a synthesizer player in performing sustained "pads". These can serve as sonic backgrounds in modern pop. Creating a pad sound differs from usual rhythm guitar roles in that it is not rhythmic. Some bands have a synthesizer
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and ...
performer play pads. In bands without a synth player, a guitarist can take over this role.
Replacing lead guitar
Some rhythm techniques cross over intolead guitar
Lead guitar (also known as solo guitar) is a musical part for a guitar in which the guitarist plays melody lines, instrumental fill passages, guitar solos, and occasionally, some riffs and chords within a song structure. The lead is the featur ...
playing. In guitar-bass-and-drums power trio
A power trio is a rock and roll band format having a lineup of electric guitar, bass guitar and drum kit (drums and cymbals), leaving out a second rhythm guitar or keyboard instrument that are often used in other rock music bands that are quartet ...
s guitarists must double up between rhythm and lead. For instance Jimi Hendrix
James Marshall "Jimi" Hendrix (born Johnny Allen Hendrix; November 27, 1942September 18, 1970) was an American guitarist, singer and songwriter. Although his mainstream career spanned only four years, he is widely regarded as one of the most ...
combined full chords with solo lick
Lick may refer to:
* Licking, the action of passing the tongue over a surface
Places
* Lick (crater), a crater on the Moon named after James Lick
* 1951 Lick, an asteroid named after James Lick
* Lick Township, Jackson County, Ohio, United State ...
s, double stop
In music, a double stop is the technique of playing two notes simultaneously on a stringed instrument such as a violin, a viola, a cello, or a double bass. On instruments such as the Hardanger fiddle it is common and often employed. In performin ...
s and arpeggio
A broken chord is a chord broken into a sequence of notes. A broken chord may repeat some of the notes from the chord and span one or more octaves.
An arpeggio () is a type of broken chord, in which the notes that compose a chord are played ...
s. In recent years, " looping pedals" have been used to supply chord sequences or riffs over which musicians can then play the lead line, simulating the sound achieved by having two guitarists.
Equipment
A rhythm guitarist usually aims to generate a strong rhythmic and chordal sound, in contrast to the lead guitarist's goal of producing sustained, often higher-pitched melody lines, that listeners can distinguish above the other instruments. As a result, rhythm and lead players often use different guitars and amplifiers. Rhythm guitarists may employ an electricacoustic guitar
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, ...
or a humbucker
A humbucking pickup, humbucker, or double coil, is a type of guitar pickup that uses two wire coils to cancel out the noisy interference picked up by coil pickups. In addition to electric guitar pickups, humbucking coils are sometimes used in d ...
-equipped electric guitar for a richer and fatter output. Also, rhythm guitarists may use strings of a larger gauge than those used by lead guitarists. However, while these may be practices, they are not necessarily the rule and are subject to the style of the song and the preference of the individual guitarist.
While rhythm guitarists in metal bands use distortion effects, they tend to use less of the modulation effects such as flangers used by lead guitar players. Whereas the lead guitarist in a metal band is trying to make the solo tone more prominent, and thus uses a range of colorful effects, the rhythm guitarist is typically trying to provide a thick, solid supporting sound that blends in with the overall sound of the group. In alternative rock and post-punk, however, where the band may be aiming to create an ambient soundscape rather than an aggressive Motörhead
Motörhead () were an English rock band formed in London in 1975 by Lemmy (lead vocals, bass), Larry Wallis (guitar) and Lucas Fox (drums). Lemmy was also the primary songwriter and only constant member. The band are often considered a precu ...
-style "Wall of Sound
The Wall of Sound (also called the Spector Sound) is a music production formula developed by American record producer Phil Spector at Gold Star Studios, in the 1960s, with assistance from engineer Larry Levine and the conglomerate of session m ...
", the rhythm guitarist may use flanging and delay effects to create a shimmering background, or (as in The Smiths
The Smiths were an English rock band formed in Manchester in 1982. They comprised the singer Morrissey, the guitarist Johnny Marr, the bassist Andy Rourke and the drummer Mike Joyce. They are regarded as one of the most important acts to emerg ...
song "How Soon Is Now?
"How Soon Is Now?" is a song by English rock band the Smiths, written by singer Morrissey and guitarist Johnny Marr. Originally a B-side of the 1984 single "William, It Was Really Nothing", "How Soon Is Now?" was subsequently featured on the co ...
"), a reverberating tremolo effect.
Jazz
Rhythm guitar has been especially important in the development of jazz. The guitar took over the role previously occupied by the banjo to provide rhythmic chordal accompaniment. Early jazz guitarists like Freddie Green tended to emphasize the percussive quality of the instrument. The ability to keep a steady rhythm while playing through complicated chord patterns made the guitar invaluable to many rhythm sections. Jazz guitarists are expected to have deep knowledge of harmony.Jazz harmony
Jazz guitar
Jazz guitar may refer to either a type of electric guitar or a guitar playing style in jazz, using electric amplification to increase the volume of acoustic guitars.
In the early 1930s, jazz musicians sought to amplify their sound to be hear ...
ists use their knowledge of harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However ...
and jazz theory to create jazz chord "voicings", which emphasize the 3rd and 7th notes of the chord. Unlike pop and rock guitarists, who typically include the root of a chord (even, with many open chords and barre chords, doubling the root), jazz guitarists typically omit the root. Some more sophisticated chord voicings also include the 9th, 11th, and 13th notes of the chord. A typical jazz voicing for the chord G7 would be the individual notes B, E, F, and A. This voicing uses the 3rd (the note B), the 7th (the note F), along with the 6th (the note E) and the 9th (the note A).
In some modern jazz styles, dominant 7th
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad tog ...
chords in a tune may contain altered 9ths (either flattened by a semitone, which is called a "flat 9th", or sharpened by a semitone, which is called a "sharp 9th"); 11ths (sharpened by a semitone, which is called a "sharp 11th"); 13ths (typically flattened by a semitone, which is called a "flat 13th").
Jazz guitarists need to learn about a range of different chords, including major 7th
In music, a major seventh chord is a seventh chord in which the third is a major third above the root and the seventh is a major seventh above the root. The major seventh chord, sometimes also called a ''Delta chord'', can be written as maj7, M7, , ...
, major 6th
In music from Western culture, a sixth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing six note letter names or staff positions (see Interval (music)#Number, Interval number for more details), and the major sixth is one of two commonly occ ...
, minor 7th
In music theory, a minor seventh is one of two musical intervals that span seven staff positions. It is ''minor'' because it is the smaller of the two sevenths, spanning ten semitones. The major seventh spans eleven. For example, the interval f ...
, minor/major 7th, dominant 7th
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad tog ...
, diminished, half-diminished, and augmented chord
Augment or augmentation may refer to:
Language
*Augment (Indo-European), a syllable added to the beginning of the word in certain Indo-European languages
*Augment (Bantu languages), a morpheme that is prefixed to the noun class prefix of nouns i ...
s. As well, they need to learn about chord transformations (e.g., altered chords, such as "alt dominant chords" described above), chord substitution
In music theory, chord substitution is the technique of using a chord in place of another in a progression of chords, or a chord progression. Much of the European classical repertoire and the vast majority of blues, jazz and rock music songs a ...
s, and re-harmonization techniques. Some jazz guitarists use their knowledge of jazz scales and chords to provide a walking bass
Bassline (also known as a bass line or bass part) is the term used in many styles of music, such as blues, jazz, funk, Dub music, dub and electronic music, electronic, traditional music, traditional, or classical music for the low-pitched Part ( ...
-style accompaniment.
Jazz guitarists learn to perform these chords over the range of different chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice ...
s used in jazz, such as the II-V-I progression, the jazz-style blues progression
The 12-bar blues (or blues changes) is one of the most prominent chord progressions in popular music. The blues progression has a distinctive form in lyrics, phrase, chord structure, and duration. In its basic form, it is predominantly based on ...
, the minor jazz-style blues form, the "rhythm changes
Rhythm changes are a common 32-bar chord progression in jazz, originating as the chord progression for George Gershwin's "I Got Rhythm". The progression is in AABA form, with each A section based on repetitions of the ubiquitous I–vi–ii–V s ...
" progression, and the variety of chord progressions used in jazz ballads, and jazz standard
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are an important part of the musical repertoire of jazz musicians, in that they are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz musicians, and widely known by listeners. There is no definitive lis ...
s. Guitarists may also learn to use the chord types, strumming styles, and effects pedal
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in ele ...
s (e.g., chorus effect
Chorus (or chorusing, choruser or chorused effect) is an audio effect that occurs when individual sounds with approximately the same time, and very similar pitches, converge. While similar sounds coming from multiple sources can occur naturally, ...
or fuzzbox
Distortion and overdrive are forms of audio signal processing used to alter the sound of amplified electric musical instruments, usually by increasing their gain, producing a "fuzzy", "growling", or "gritty" tone. Distortion is most commonly ...
) used in 1970s-era jazz-Latin, jazz-funk, and jazz-rock fusion music.
Big band rhythm
In jazzbig band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s an ...
s, popular during the 1930s and 1940s, the guitarist is considered an integral part of the rhythm section (guitar, drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a she ...
s and bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in the bass range:
** Bass (instrument), including:
** Acoustic bass gui ...
). They usually played a regular four chords to the bar, although an amount of harmonic improvisation is possible. Freddie Green
Frederick William Green (March 31, 1911 – March 1, 1987) was an American swing jazz guitarist who played rhythm guitar with the Count Basie Orchestra for almost fifty years.
Early life and education
Green was born in Charleston, South Ca ...
, guitarist in the Count Basie
William James "Count" Basie (; August 21, 1904 – April 26, 1984) was an American jazz pianist, organist, bandleader, and composer. In 1935, he formed the Count Basie Orchestra, and in 1936 took them to Chicago for a long engagement and the ...
orchestra, was a noted exponent of this style. The harmonies are often minimal; for instance, the root note
In music theory, the concept of root is the idea that a chord can be represented and named by one of its notes. It is linked to harmonic thinking—the idea that vertical aggregates of notes can form a single unit, a chord. It is in this sense ...
is often omitted on the assumption that it will be supplied by the bassist.
Small group comping
When jazz guitarists play chords underneath a song's melody or another musician's solo improvisations, it is called '' comping'', short for ''accompanying''. The accompanying style in most jazz styles differs from the way chordal instruments accompany in many popular styles of music. In many popular styles of music, such as rock and pop, the rhythm guitarist usually performs the chords in rhythmic fashion which sets out the beat or groove of a tune. In contrast, in many modern jazz styles within smaller, the guitarist plays much more sparsely, intermingling periodic chords and delicate voicings into pauses in the melody or solo, and using periods of silence. Jazz guitarists commonly use a wide variety of inversions when comping, rather than only using standard voicings.Gypsy pumping

Gypsy jazz
Gypsy jazz (also known as gypsy swing, jazz manouche or hot club-style jazz) is a style of small-group jazz originating from the Romani guitarist Jean "Django" Reinhardt (1910–53), in conjunction with the French swing violinist Stéphane Gr ...
is acoustic music, usually played without a drummer. Rhythm guitar in gypsy jazz
Gypsy jazz (also known as gypsy swing, jazz manouche or hot club-style jazz) is a style of small-group jazz originating from the Romani guitarist Jean "Django" Reinhardt (1910–53), in conjunction with the French swing violinist Stéphane Gr ...
uses a special form of strumming
In music, strumming is a way of playing a stringed instrument such as a guitar, ukulele, or mandolin. A strum or stroke is a sweeping action where a finger or plectrum brushes over several Strings (music), strings to generate sound. On most st ...
known as "la pompe
Gypsy jazz (also known as gypsy swing, jazz manouche or hot club-style jazz) is a style of small-group jazz originating from the Romani guitarist Jean "Django" Reinhardt (1910–53), in conjunction with the French swing violinist Stéphane Gr ...
", i.e. "the pump". This form of percussive rhythm is similar to the "boom-chick" in bluegrass styles; it is what gives the music its fast swinging feeling. The strumming hand, which never touches the top of the guitar, must make a quick up-down strum followed by a down strum. The up-down part of la pompe must be done extremely fast, regardless of the tempo of the music. It is very similar to a grace note in classical music, albeit the fact that an entire chord is used. This pattern is usually played in unison by two or more guitarists in the rhythm section.
Jazz chord soloing
Jazz guitar soloists are not limited to playing single notes by their instrument. This allows them to create "chord solos" by adding the song's melody on top of the chord voicings.Wes Montgomery
John Leslie "Wes" Montgomery (March 6, 1923 – June 15, 1968) was an American jazz guitarist. Montgomery was known for an unusual technique of plucking the strings with the side of his thumb and his extensive use of octaves, which gave him a dist ...
was noted for playing successive choruses in single notes, octaves and finally a chord solo. This technique differs from chord-melody soloing in that it is not intended to be used unaccompanied
Funk
 Funk utilized the same
Funk utilized the same extended chords
In music, extended chords are certain chords (built from thirds) or triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh. Ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonical ...
found in bebop
Bebop or bop is a style of jazz developed in the early-to-mid-1940s in the United States. The style features compositions characterized by a fast tempo, complex chord progressions with rapid chord changes and numerous changes of key, instrumen ...
jazz, such as minor chords with added sevenths and elevenths, or dominant seventh chords with altered ninths. However, unlike bebop jazz, with its complex, rapid-fire chord changes, funk virtually abandoned chord changes, creating static single chord vamps with little harmonic movement, but with a complex and driving rhythmic feel. Some have jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major ...
backgrounds. The chords used in funk songs typically imply a dorian or mixolydian mode
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scal ...
, as opposed to the major or natural minor tonalities of most popular music. Melodic content was derived by mixing these modes with the blues scale
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the African- ...
.
In funk bands, guitarists typically play in a percussive style, often using the wah-wah sound effect and muting the notes in their riffs to create a percussive sound. Guitarists Ernie Isley
Ernest Isley (born March 7, 1952) is an American musician, best known as a member of the musical ensemble The Isley Brothers, and also the splinter group Isley-Jasper-Isley.
Biography
Ernie was born in Cincinnati, where his older brothers for ...
of The Isley Brothers
The Isley Brothers ( ) are an American musical group originally from Cincinnati, Ohio, that began as a vocal trio consisting of brothers O'Kelly Isley Jr., Rudolph Isley and Ronald Isley in the 1950s. With a career spanning over seven decades, ...
and Eddie Hazel
Edward Earl Hazel (April 10, 1950 – December 23, 1992) was an American guitarist and singer in early funk music who played lead guitar with Parliament-Funkadelic. Hazel was a posthumous inductee to the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame, inducted in ...
of Funkadelic
Funkadelic was an American funk rock band formed in Plainfield, New Jersey in 1968 and active until 1982. The band and its sister act Parliament, both led by George Clinton, pioneered the funk music culture of the 1970s.John, Bush. Funkadeli ...
were notably influenced by Jimi Hendrix
James Marshall "Jimi" Hendrix (born Johnny Allen Hendrix; November 27, 1942September 18, 1970) was an American guitarist, singer and songwriter. Although his mainstream career spanned only four years, he is widely regarded as one of the most ...
's improvised solos. Eddie Hazel, who worked with George Clinton, is a notable guitar soloist in funk. Ernie Isley was tutored at an early age by Jimi Hendrix himself, when he was a part of The Isley Brothers backing band and lived in the attic temporarily at the Isleys' household. Jimmy Nolen
Jimmy Nolen (April 3, 1934 – December 18, 1983)
- accessed November 13, 2011 was an American and
 The
The
Multimedia Rhythm Guitar Lessons
Jazz Guitar Rhythms
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rhythm Guitar Guitar performance techniques Popular music Accompaniment Guitars Rhythm and meter it:Chitarra#Chitarra ritmica
- accessed November 13, 2011 was an American and
Phelps Collins
Phelps "Catfish" Collins (October 17, 1943 – August 6, 2010) was an American musician. A lead guitarist and rhythm guitarist, he is known mostly for his work in the P-Funk collective. Although frequently overshadowed by his younger brother, ...
are famous funk rhythm guitarists who both worked with James Brown
James Joseph Brown (May 3, 1933 – December 25, 2006) was an American singer, dancer, musician, record producer and bandleader. The central progenitor of funk music and a major figure of 20th century music, he is often referred to by the honor ...
.
Reggae
 The
The guitar
The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected stri ...
in reggae usually plays the chords on beats two and four, a musical figure known as skank or the 'bang'. It has a very dampened, short and scratchy chop
Chop, CHOP, Chops, or CHOPS may refer to:
Art
*Embouchure, in music, a synonym for chops (and later, more broadly, musical skill or ability)
*CHOPS, an Asian-American hip hop producer, rapper and member of rap group Mountain Brothers
* ''Chops'' ...
sound, almost like a percussion instrument. Sometimes a double chop is used when the guitar still plays the off beats, but also plays the following 16th or 8th beat on the up-stroke. Depending on the amount of swing or groove, this next secondary stab is often the 16th note sounding closer to an 8th placement in the rhythm. An example is the intro to "Stir It Up
"Stir It Up" is a song composed by Bob Marley in 1967 and first recorded by the group Bob Marley and the Wailers that year and issued as a single. It was later covered by American singer Johnny Nash on his 1972 album ''I Can See Clearly Now'' ...
" by The Wailers
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
. Artist and producer Derrick Harriott
Derrick Clifton Harriott Order of Distinction, OD (born 10 February 1942) is a Jamaican singer and record producer. He was a member of the Jiving Juniors with Herman Sang before embarking on a solo career. He has produced sound recording and re ...
says, "What happened was the musical thing was real widespread, but only among a certain sort of people. It was always a down-town thing, but more than just hearing the music. The equipment was so powerful and the vibe so strong that we feel it."Bradley, Lloyd. ''This Is Reggae Music:The Story Of Jamaica's Music.'' New York:Grove Press, 2001 Reggae chords are typically played without overdrive or distortion.
See also
*List of rhythm guitarists
The following is a list of notable rhythm guitarists, arranged in ascending alphabetical order of last name.
Rhythm guitarists perform a combination of two functions: they provide all or part of the rhythmic pulse in conjunction with other rhythm ...
* Flamenco guitar
A flamenco guitar is a guitar similar to a classical guitar but with thinner tops and less internal bracing. It usually has nylon strings, like the classical guitar, but it generally possesses a livelier, more gritty sound compared to the clas ...
* Steel guitar
A steel guitar ( haw, kīkākila) is any guitar played while moving a steel bar or similar hard object against plucked strings. The bar itself is called a "steel" and is the source of the name "steel guitar". The instrument differs from a conve ...
* John Lennon
John Winston Ono Lennon (born John Winston Lennon; 9 October 19408 December 1980) was an English singer, songwriter, musician and peace activist who achieved worldwide fame as founder, co-songwriter, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of ...
References
External links
Multimedia Rhythm Guitar Lessons
Jazz Guitar Rhythms
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rhythm Guitar Guitar performance techniques Popular music Accompaniment Guitars Rhythm and meter it:Chitarra#Chitarra ritmica